Cybersecurity Threats That Target Insurance Companies In an increasingly digital world, insurance companies are facing a growing number of cybersecurity threats. These threats not only put sensitive customer data at risk but also jeopardize the financial stability and reputation of the companies themselves. In this article, we will explore some of the most prominent cybersecurity threats that target insurance companies and discuss the importance of robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate these risks.
Data Breache

Data breaches are one of the most significant cybersecurity threats faced by insurance companies. These breaches can result in the exposure of sensitive customer information, including personal details, financial records, and medical histories. Cybercriminals often target insurance companies with the intent of stealing this valuable data for various purposes, such as identity theft, fraud, or selling it on the dark web.
To combat data breaches, insurance companies must invest in robust encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring of their networks. Regular employee training on cybersecurity best practices is also essential to prevent phishing attacks that can lead to data breaches.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly prevalent in recent years, and insurance companies are prime targets. In a ransomware attack, cybercriminals encrypt a company’s data and demand a ransom in exchange for the decryption key. These attacks can disrupt operations, lead to data loss, and result in substantial financial losses.
Insurance companies need to implement strong backup and recovery solutions to ensure data can be restored without paying the ransom. Moreover, proactive measures such as network segmentation and robust email filtering can help prevent ransomware from infiltrating their systems in the first place.
Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks, which rely on manipulating individuals within the organization, pose a significant threat to insurance companies. Phishing, pretexting, and baiting are common tactics used by cybercriminals to trick employees into revealing sensitive information or granting access to corporate systems.
Insurance companies should conduct regular cybersecurity training and awareness programs to educate employees about the dangers of social engineering attacks. Implementing strict policies for verifying the identity of individuals requesting sensitive information or access can also help mitigate this threat.
Third-Party Risk
Insurance companies often work with a network of third-party vendors and partners, each of which can introduce vulnerabilities into their systems. Cybercriminals may target these third parties as a means to infiltrate the insurance company’s network. A breach in a vendor’s system can have far-reaching consequences for the insurance company’s security.
To address third-party risk, insurance companies should conduct thorough cybersecurity assessments of their vendors and partners. Contracts should include specific cybersecurity requirements and provisions for reporting and mitigating breaches promptly.
Insider Threats
Insider threats can be particularly challenging for insurance companies to detect and prevent.
These threats involve employees or other individuals with inside access to the company’s systems intentionally or unintentionally compromising security.
This could be through malicious actions, negligence, or a lack of awareness.
To mitigate insider threats, insurance companies should implement strong access controls and monitor user activity within their networks. Employee training and awareness programs should emphasize the importance of cybersecurity and the consequences of insider threats.
As insurance companies continue to embrace digital technologies and collect vast amounts of sensitive customer data, they become increasingly attractive targets for cybercriminals. To protect their customers, reputation, and financial stability, insurance companies must prioritize cybersecurity. By investing in robust security measures, employee training, and proactive risk management strategies, insurance companies can better defend against the evolving cyber threats that they face in today’s digital landscape. Cybersecurity is not just an option; it’s a necessity in the insurance industry.
The Cybersecurity Roadmap
A well-defined cybersecurity roadmap is essential for insurance companies looking to protect their digital assets effectively. This roadmap should outline a strategic plan for enhancing cybersecurity measures over time. It might include key milestones, budget allocations, and the adoption of emerging technologies and practices. Continuous monitoring and regular updates to the roadmap are crucial as the threat landscape evolves.
Cybersecurity Courses and Training
To build a robust cybersecurity defense, insurance companies should invest in training their employees and IT teams. Cybersecurity courses, both in-house and external, can help individuals develop the skills and knowledge required to identify and mitigate threats effectively. Some employees might consider pursuing professional certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) to enhance their cybersecurity credentials.
What Is Cybersecurity?
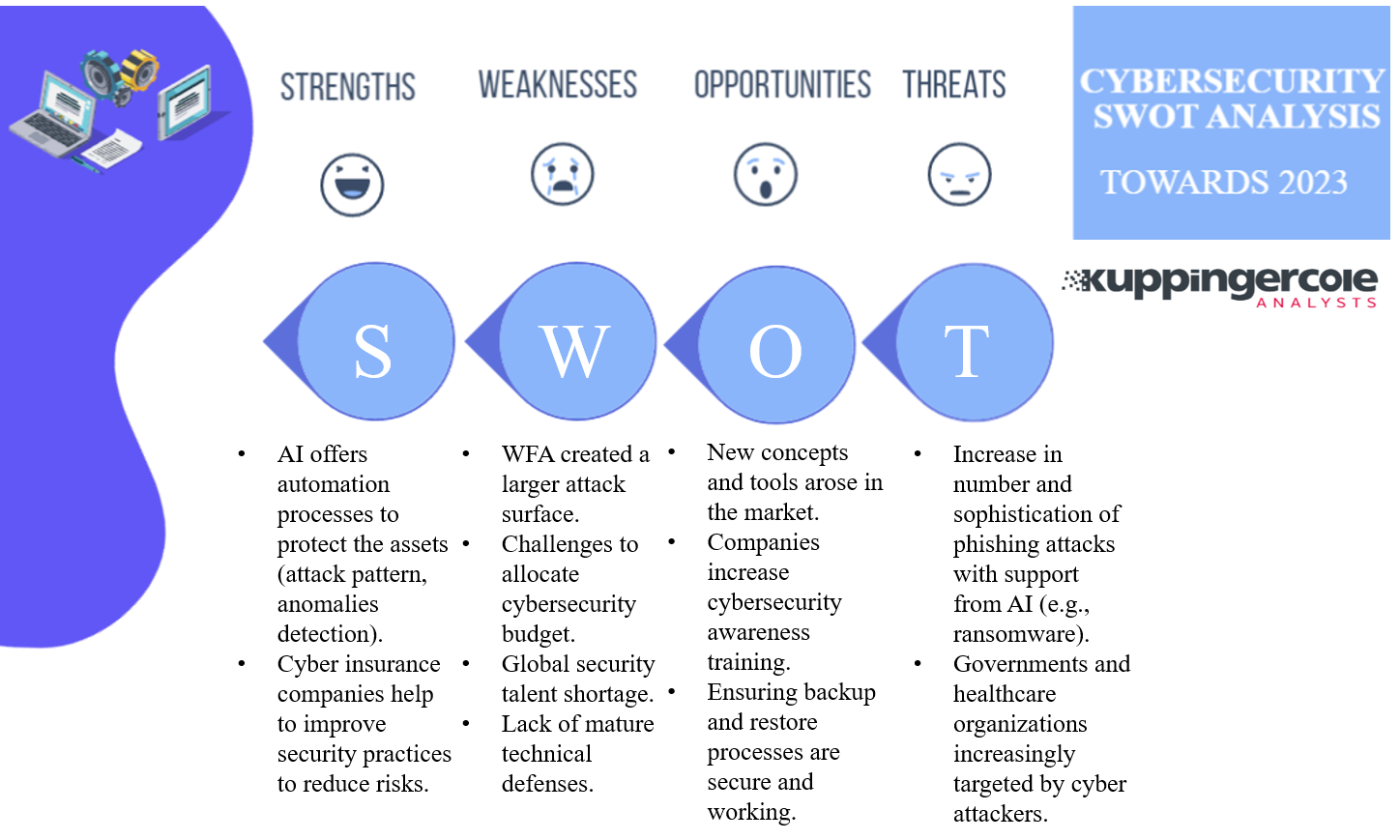
Cybersecurity encompasses the practices, technologies, and processes used to protect digital systems, networks, and data from theft, damage, or unauthorized access. It involves a wide range of strategies, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, access controls, and incident response plans. The ultimate goal of cybersecurity is to safeguard information and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital assets.
Cybersecurity Salaries
Cybersecurity professionals are in high demand worldwide, and this demand extends to Egypt as well. Salaries in the cybersecurity field can vary significantly based on experience, certifications, and specific roles. In Egypt, entry-level cybersecurity analysts may earn around EGP 50,000 to EGP 80,000 per year, while more experienced professionals such as cybersecurity managers or specialists with advanced certifications can earn EGP 120,000 or more annually.
Cybersecurity Jobs
The demand for cybersecurity experts is steadily growing, and insurance companies in Egypt are no exception. Cybersecurity jobs in the insurance sector encompass roles like cybersecurity analysts, incident responders, penetration testers, security architects, and compliance officers. These professionals play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive customer data and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Free Cybersecurity Courses
For individuals interested in pursuing a career in cybersecurity, there are numerous free online courses and resources available. These courses cover a wide range of topics, from basic cybersecurity fundamentals to advanced threat analysis. Some reputable platforms offering free cybersecurity courses include Cybrary, Coursera, edX, and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
read more :Dell Inspiron 14: A Compact Powerhouse from Dell
Cybersecurity Companies in Egypt
Egypt has seen a growth in the cybersecurity sector, with several companies offering cybersecurity solutions and services.
These companies specialize in areas such as threat detection, vulnerability assessment, and security consulting.
Some notable cybersecurity companies in Egypt include Checkmarx, CyberTalents, and SecureMisr, which provide various cybersecurity services to organizations, including insurance companies.
as insurance companies face an ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, it’s imperative that they prioritize and invest in cybersecurity measures.
Building a robust cybersecurity roadmap, providing training and education, and staying informed about industry trends are essential steps to protect their digital assets and customer data effectively.
Moreover, cybersecurity professionals in Egypt have opportunities for rewarding careers in a field that plays a critical role in safeguarding businesses and individuals from cyber threats.